
|

|
 |
|
MEDICINE FROM NATURE |
| (Chapter one) |
| THE FUTURE OF MEDICINE |
| Persistent health problems at the start of the 21st century
|
|
It is obvious that many health problems still exist today and there is a need for newer, more effective
drugs with far less dangerous side effects than the flood of drugs, many with exotic commercial names, that are used today. They also work more on the symptoms than on the root cause of the (health) problem. There is an urgent need to utilize plants, fungi and molds that were used for centuries by traditional healers.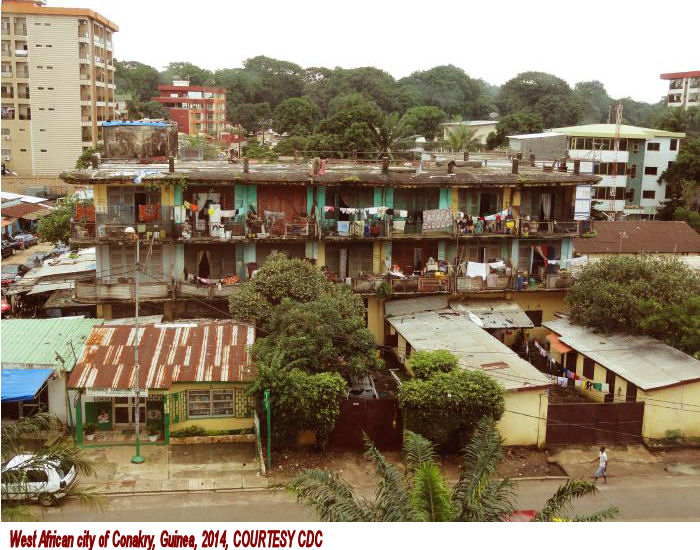  However there are unfortunately also other factors to take into account such as the state of the health care systems in
the developed world (rich countries) and Third World (poor
countries). Both face major but different challenges.
However there are unfortunately also other factors to take into account such as the state of the health care systems in
the developed world (rich countries) and Third World (poor
countries). Both face major but different challenges.Even in the most developed countries, such as the USA, access to quality care is often outrageous expensive, while in the Third World many people have no access to whatever system at all. Partly due to this reason, epidemic and pandemics often starts in underdeveloped countries in Africa. The rapid growing world population, especially in the Third World, is also a very worrying situation that needs to be addressed. People in these countries are for a great part only served by local healers working with medicinal plants and herbs gathered in the vicinity from where they practice. 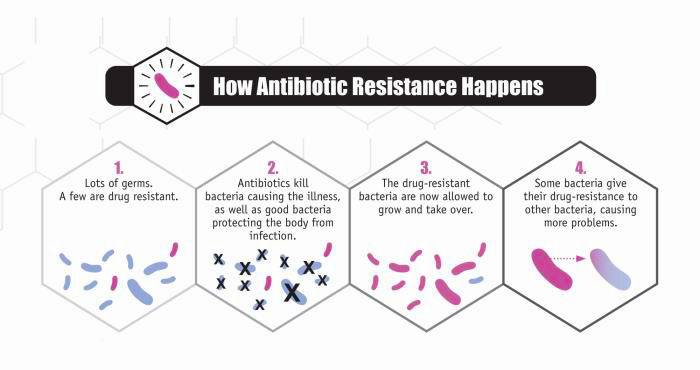 Other specific problems such as the overuse of antibiotics resulting in resistance of bacteria against these are
another world-wide problem.
Other specific problems such as the overuse of antibiotics resulting in resistance of bacteria against these are
another world-wide problem.Each year in the United States alone, at least 2 million people acquire serious infections with bacteria that are resistant to one or more of the antibiotics designed to treat those infections. At least 23,000 people die each year as a direct result of these antibiotic-resistant infections. Many more die from other conditions that were complicated by an antibiotic- resistant infection. The overuse of antibiotics is the single most important factor leading to antibiotic resistance around the world. Antibiotics are among the most commonly prescribed drugs used in human medicine. However, up to 50% of all the antibiotics prescribed for people are not needed, or are not optimally effective as prescribed. Antibiotics are also commonly used in food for animals to prevent, control, and treat diseases, as well to promote the growth of food-producing animals. (CDC/ Melissa Brower). The WHO cautioned in a 2014 report: A post-antibiotic era -- in which common infections and minor injuries can kill, far from being an apocalyptic fantasy, is instead a very real possibility for the 21st century. According to the CDC,1 in 3 antibiotic prescriptions are unnecessary.  “Antibiotics are lifesaving drugs, and if we continue down the road of inappropriate use we’ll lose the most powerful tool we have to
fight life-threatening infections,” said CDC Director Tom Frieden, M.D, M.P.H. “Losing these antibiotics would undermine our ability to
treat patients with deadly infections, cancer, provide organ transplants, and save victims of burns and trauma.”
“Antibiotics are lifesaving drugs, and if we continue down the road of inappropriate use we’ll lose the most powerful tool we have to
fight life-threatening infections,” said CDC Director Tom Frieden, M.D, M.P.H. “Losing these antibiotics would undermine our ability to
treat patients with deadly infections, cancer, provide organ transplants, and save victims of burns and trauma.”Antibiotics These are chemical compounds that inhibit the growth of microorganisms. Most antibiotics are only anti-bacterial and do not have activity against viruses, fungi and other microbes. They also kill friendly bacteria in the colon. Ancient healers were keenly aware of certain substances having antibiotic properties; however they did not understand what caused infection. It was not until the start on the 19th century that mankind knew that bacteria were the culprit. One of the first natural medicines was used by the ancient Egyptians. It was a mixture of lard, honey and lint that was pressed into wounds. Enzymes found in the honey converts glucose and oxygen together into hydrogen peroxide, a very well known disinfectant. We now know that honey also kills the bacteria by drawing water out of them. In the Dark Ages in Europe, moldy bread was used on wounds to heal or prevent infection. The use of molds (or moulds) was also practiced in China and India. Penicillin, one of the first modern (natural) antibiotics was isolated from a piece of moldy bread. This "discovery" did not happen until 1928.  Alexander Fleming (1881-1955) was the first to suggest that the Penicillium mold secreted an antibacterial substance and
was also first to concentrate this active substance; he called it Penicillin.
Alexander Fleming (1881-1955) was the first to suggest that the Penicillium mold secreted an antibacterial substance and
was also first to concentrate this active substance; he called it Penicillin.Prescribed antibiotics kill all bacteria and do not discriminate between good and the bad one. This leaves the body stripped of its natural ability to fight infection and ward off illnesses and diseases. Shamans and other traditional healers in the Amazon rainforest use a variety of molds, not known to modern science, to treat - and prevent certain infections. Take garlic for instance; it contains many antioxidants and is perfectly suited to protect against cough, cold and flu. Garlic has the compound Allicin, that has excellent anti-bacterial, anti-viral and anti-fungal properties.  Other favorites of herbalist are without doubt Cat’s claw (Uncaria guianensis & tomentosa), Curcumin (Curcuma longa)
and Asthma weed (Euphorbia hirta).
Other favorites of herbalist are without doubt Cat’s claw (Uncaria guianensis & tomentosa), Curcumin (Curcuma longa)
and Asthma weed (Euphorbia hirta).They are all very effective in fighting internal inflammations. 
Other challenges Many more challenges also still remain to be addressed. Diabetes, high blood pressure and cholesterol are nowadays almost pandemics! There are many allopathic (western) drugs out there to be used against these illnesses. Most of them though are expensive and often not very effective; some even may have serious side effects. 
 Luckily there are many botanicals available that can do the job just as good without the high price tag attached to them and even more
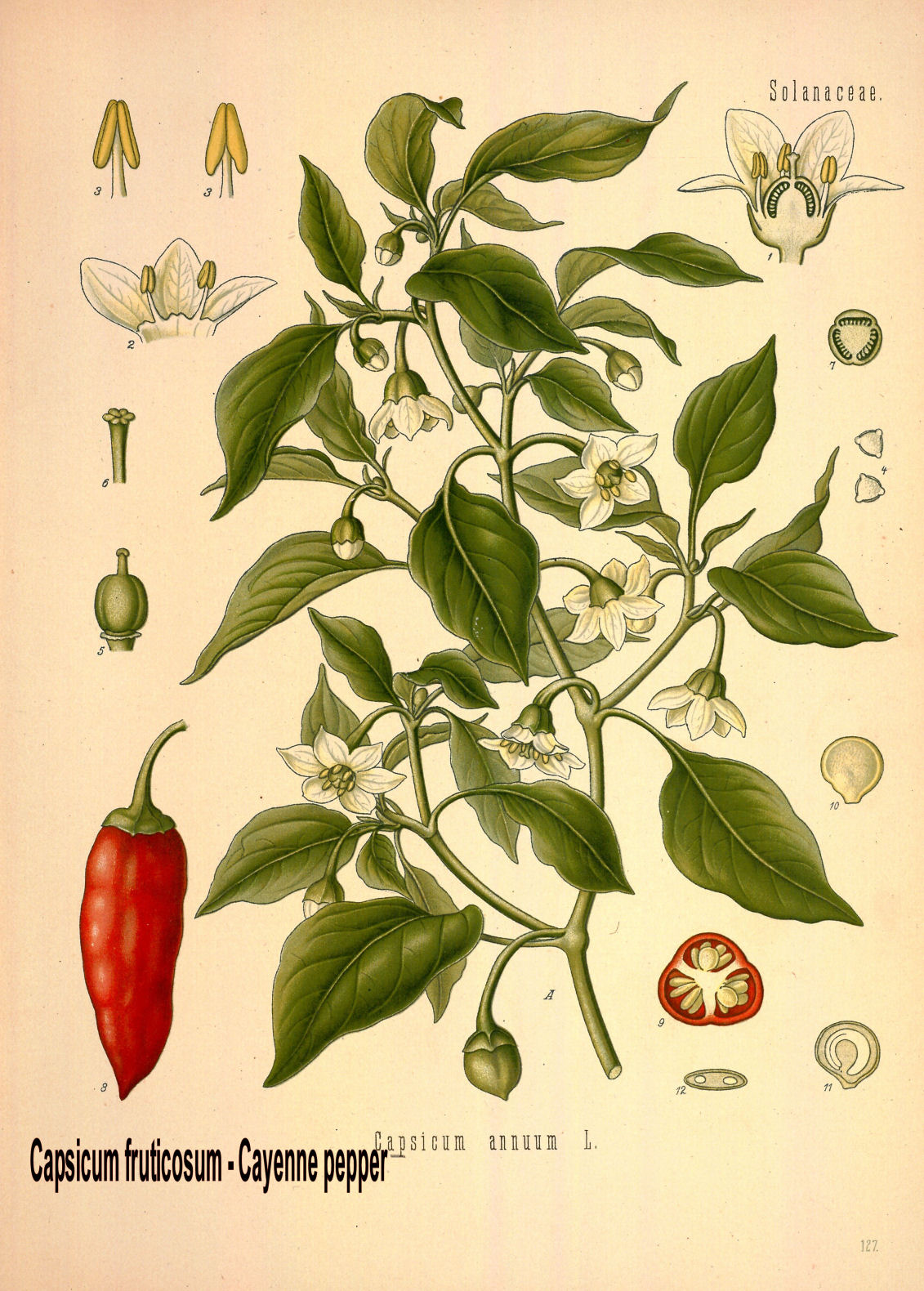
important; without these side effects. Just to name a few in this context: Banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa) against diabetes and
high triglycerides, Cayenne (Capsicum frutescens) against elevated blood pressure.
Luckily there are many botanicals available that can do the job just as good without the high price tag attached to them and even more
important; without these side effects. Just to name a few in this context: Banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa) against diabetes and
high triglycerides, Cayenne (Capsicum frutescens) against elevated blood pressure.
Treatment with natural medicine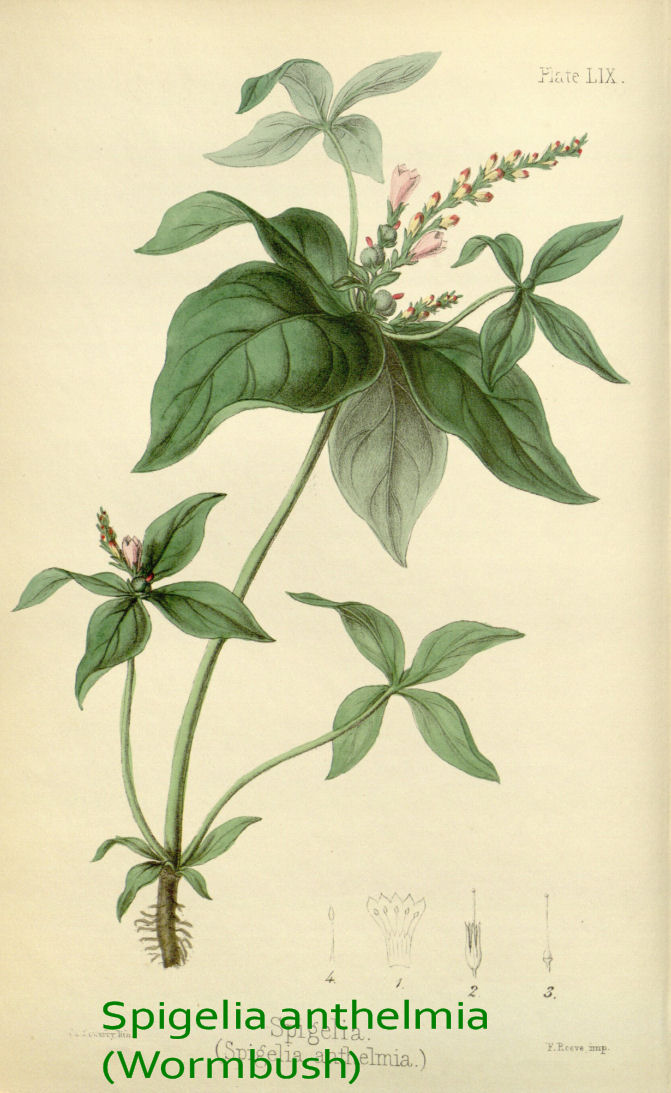  Although botanicals are generally safe and have as said, far fewer side effects, remedies from botanicals are powerful and some may even
be very toxic.
Although botanicals are generally safe and have as said, far fewer side effects, remedies from botanicals are powerful and some may even
be very toxic.One should not presume that since a product comes from nature it must be naturally safe; powerful natural poisons within the plant like atropine and nicotine belie this.  Datura stramonium (Jimson weed) has been used for asthma, because it contains the alkaloid atropine, but it is also a
powerful and potentially fatal hallucinogen.
Datura stramonium (Jimson weed) has been used for asthma, because it contains the alkaloid atropine, but it is also a
powerful and potentially fatal hallucinogen.There may be also undesirable reciprocal interactions between botanicals and allopathic drugs. Another exemple; Spigelia anthelmia (Demerara pinkroot) is a very poisonous plant but when applied by a qualified homeopathic, it exerts a powerful action on the nervous system. It also has an important role in cardiac treatment and it is a major drug for pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardium). 
 Shamans and other health practitioners specialized in this field, in general know how to effectively and safely use these botanicals.
Shamans and other health practitioners specialized in this field, in general know how to effectively and safely use these botanicals.The majority of medical doctors though has not been taught in depth, if at all, about the use of medicinal plants and often consider themselves not qualified to give patients the right advice. Fortunately though, these days there is an upward trend to train more specialists in the science of alternative medicine who are indeed qualified to give the right advice to patients for the use and treatment of botanicals against their health problems. |
Disclaimer: |