 |
|
HEPATITIS Natural Herbal Treatment and Prevention from AMAZON HERBS® 
|
| Follow us online |
| |
|
Overview Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver and often caused by a virus. It can also be caused by medications, toxins, (heavy) alcohol use and certain medical conditions such as autoimmune disorders. Inflammation of the liver, the largest organ in the body, is serious, has profound consequences and eventually may cause liver cirrhosis and cancer. Hepatitis B and C are caused by viruses and together kill approximately one million people a year in the U.S.; 500 million people around the world are now infected with chronic hepatitis B or C. Symptoms may start to appear 4 - 5 weeks after infection, however a majority of those infected donít show any symptoms. 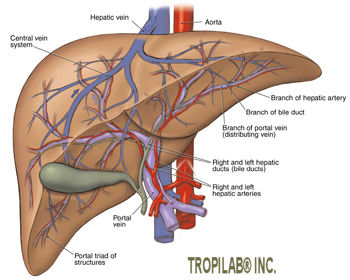 There are two types of hepatitis:
There are two types of hepatitis:Acute- and Chronic hepatitis. Acute hepatitis (fulminant hepatic failure); initial features are of nonspecific flu-like symptoms. There is no specific treatment for any form of acute hepatitis; after some time acute hepatitis can turn into chronic hepatitis. Chronic hepatitis; often has nonspecific symptoms (malaise, tiredness and weakness), and shows no symptoms at all. It is commonly identified by taking blood tests. There are also secondary effects such as allergies, cancer, high cholesterol, etc. Currently there are 7 known viruses that cause hepatitis. Hepatitis A The symptoms look a lot like those of common gastroenteritis or a viral infection of the bowel. Most people that get Hepatitis A have no symptoms whatsoever; it is a virus and is spread through contact with fecal matter (often spread through person to person contact). There is no known treatment for this type of hepatitis but if somebody gets it, he or she will develop antibodies to it that will last for the rest of the personís life. Usually it lasts less than 2 months; however, symptoms can last up to 6 months.  Hepatitis B
Hepatitis BHepatitis B virus (HBV) is transmitted between people through contact with blood or other body fluids (such as saliva, semen and vaginal fluid) of an infected person. Infection can also occur by having unprotected sex with an infected person. Hepatitis C Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is contagious; it spread through direct contact with infected blood. About 170 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C; this virus is one of the leading known causes of liver disease in the United States. This virus (HCV) can lie dormant for years, while damaging the liver, before it becomes symptomatic. There may be potentially fatal consequences. Also, drinking may worsen the infection. Hepatitis D Hepatitis D virus (HDV); this disease is caused by a small circular enveloped RNA virus. It can propagate only in the presence of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). In combination with hepatitis B virus, hepatitis D has the highest mortality rate of all the hepatitis infections. The routes of transmission of hepatitis D are similar to those for hepatitis B. The infection is largely restricted to persons at high risk of hepatitis B infection. Hepatitis E Hepatitis E virus (HEV); this disease is caused by the hepatitis E virus: a single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus. This virus is transmitted mainly through contaminated drinking water. Normally it is a self-limiting infection and resolves within 4Ė6 weeks. Hepatitis F A hypothetical virus linked to hepatitis. However, an infection found in the Far East has shown a new virus which is neither hepatitis B nor C. Hepatitis G GBV-C, another potential viral cause of hepatitis; this virus, has been identified and is probably spread by blood and sexual contact. Often patients with hepatitis G are infected at the same time by the hepatitis B or C virus, or both. Conventional Treatment of Hepatitis When it comes to western medicine, there is not much to offer for hepatitis patients other than blood tests, biopsies and treatment with only a few drugs. At this time, vaccination is only available to protect against hepatitis A and hepatitis B. These forms of the disease are caused by viral infections. No vaccine is available for hepatitis C. The prescription drugs usually used for treating hepatitis C are interferons combined with ribavirin and a protease inhibitor (boceprevir ledipasvir/sofosbuvir or telaprevir). However, these drugs don't always work and they can have serious side effects (depression, weight loss, and autoimmune disease). Ginger may help patients to tolerate pegylated interferon and ribavirin, increasing their likelihood of success with the treatment. A preventative vaccine (HEV 239) for Hepatitis E is used in China. Natural Treatment of Hepatitis with herbal dietary supplements There are many (tropical) botanicals that can be employed in the alternative and complementary treatment of hepatitis. We have on our list plants originating from the Amazon rainforest and South-east Asia. Some use them as an alternative to traditional prescription drugs and/or in combination with these. Boost the immunity system which is very important in viral diseases. An Ayurvedic herb and one of the best working plants against hepatitis B and C, by reducing increased liver enzymes and helps stopping the virus from replicating. It has specific antiviral properties and may be used alone or in combination with an antiviral drug. Used by Ayurvedic practitioners for more than 3,000 years against fatty liver and liver cirrhosis. It can inhibit the growth of hepatitis B virus by down-regulating the protein complex (NF-kB), responsible for the multiplication of this virus. It has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for more than 1000 years. Can be employed as an effective alternative and complementary treatment against Hepatitis C; effectively inhibited HCV replication which resulted in reduced HCV RNA titer and translation level of viral proteins. Fedegoso extracts can protect the liver from introduced chemical toxins, normalize liver enzymes and repair liver damage. It has demonstrated antiviral properties against Hepatitis B, and has anti-hepatotoxic properties. By relieving nausea (a common side effect in the conventional treatment of hepatitis), ginger has the potential to help patients tolerate interferon and ribavirin, which can increase their changes of a successful Hepatitis C treatment. The fruit phytochemicals decrease hepatic inflammation and oxidative stress; protects against hepatocellular injury. This is a potential antioxidant/anti-inflammatory therapy, not only to treat cholestasis but also other liver diseases with an inflammatory component. Is a strong inhibitor of viruses (RNA and DNA genome viruses), such as Hepatitis C, A and B. Contains the phytochemicals Punicalagin and Punicalin, they exert at small doses antioxidative activity; works also against cirrhosis. |




|
||||



|
|
The above presentation is for informational and educational purposes only. It is based on scientific studies (human, animal, or in vitro), clinical experience, or traditional usage. For many of the conditions discussed, treatment with prescription or over - the - counter (OTC) medication is also available. Consult your doctor, practitioner, and/or pharmacist for any health problem and before using dietary supplements or before making any changes in prescribed medications. |
|
For translation use The Google Language Tools
|
All the information in this database is for education & information purposes
only! |
| TROPILAB® INC. P.O.BOX 48164 St.Petersburg, Florida 33743 - 8164. USA. Phone: (727) 344 - 7608. |